By Charalampos Karouzos,
Unquestionably, the popularity of plant-based diets has surged in recent years and people are turning away from their traditional diets. Although some may consider it more of a trend, various factors such as ethical concerns, environmental sustainability, and perceived health benefits, that were previously neglected are now appreciated to a higher level by a constantly rising number of people. Indeed, a meal in many cultures is the occasion to initiate a social event, and thus it must serve that purpose, neglecting the value of food as the necessary fuel for humans. However, although interest has risen regarding the nutritional benefits of vegetables rich diets, it is crucial to recognize that not all plant-based diets are created equal.
Initially, it is necessary to establish a base of understanding of the different plant-based diets now widely available. A diverse range of dietary patterns are being encountered, ranging from lacto-ovo vegetarians who exclude meat but consume dairy and eggs, to pescatarians that consume fish and even vegans who avoid all animal-derived products. Each variant of a plant-based diet has unique implications for human health since it is composed of drastically different foods and thus, must be uniquely assessed. In addition, contrary to the common belief regarding nutritional adequacy of these diets, well-planned plant-based diets can provide all the necessary nutrients for optimal health. By incorporating a wide array of plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, individuals can obtain a wealth of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytochemicals essential for maintaining overall well-being. Furthermore, plant-based diets emphasize the consumption of nutrient-dense foods, leading to higher intakes of antioxidants and phytochemicals, compounds that in fact improve overall health.
In addition to the nutritional sufficiency of plant-based diets, studies consistently demonstrate that balanced plant-based diets are associated with a decreased risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, including heart disease, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and certain types of cancer. This association relationship can be attributed to the lower intake of highly processed food, high in saturated fats and cholesterol, coupled with the higher consumption of fiber and antioxidants found abundantly in plant foods. In fact, incorporating whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, plant-based diets not only prevent the initial development of chronic diseases but promote better cardiovascular health, better blood sugar control, weight management, and a lower risk of specific cancers. Additionally, the high fiber content of these diets supports healthy digestion and intestinal microbiota balance that reduce the risk of gastrointestinal disorders.
However, vegetarian diets, although are regarded as a very healthy choice, they are not to be found without certain noteworthy shortcomings, with one of the major concerns among the vegetarian communities being the possible nutritional deficiencies. While plant-based diets can adequately meet nutritional needs, attention must be given to certain nutrients that may require careful planning, creating a new issue reaching the set nutritional goals every day. Key nutrients of concern for vegetarians include vitamin B12, iron, zinc, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are commonly found in animal-derived products and their exclusion from the diet increases the risk of deficiencies. To address this significant issue, vegetarians should ensure the inclusion of fortified foods, supplements, or specific food combinations. For example, incorporating fortified plant-based milk or cereals for vitamin B12, including legumes and whole grains for iron and zinc, and consuming calcium-rich plant foods like leafy greens and fortified plant-based milk alternatives.
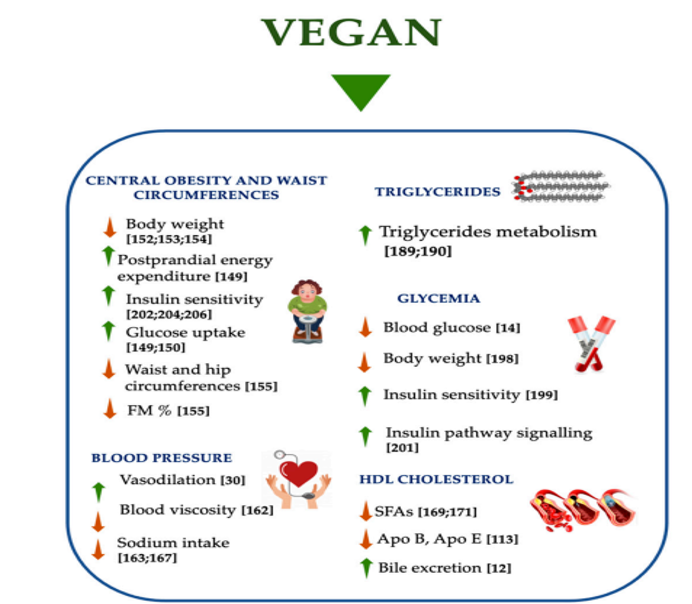
Furthermore, incorporating sufficient protein has been a concern among the non-meat- and non-fish-eating community since many plant-based protein sources may have a lower biological value and lack certain essential amino acids compared to animal sources. However, by combining different plant protein sources, such as legumes with grains or nuts and seeds, individuals can ensure the intake of all essential amino acids. It is also necessary to consume an adequate quantity of protein to meet daily requirements and support optimal health, that can be assisted by incorporating vegan protein supplements. In fact, there are several vegan athletes that have published their nutritional plans, proving that they can reach their high protein goals by avoiding animal-derived food.
Many have argued that since humans are omnivores, vegetarian diets are coming out short to the natural way of eating, and there is a truth to that point, however since people can have sufficient nutritionally plant-based diets why should they be forced to consume meat? Many individuals choose plant-based diets due to ethical concerns related to animal welfare and environmental sustainability. By abstaining from animal products, vegetarians reduce their contribution to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and animal exploitation and further their dietary choices promote a sense of personal integrity and align with moral values. Moreover, embracing plant-based diets contributes to a more sustainable food system, alleviating the strain on natural resources, preserving biodiversity, and combating climate change.
Despite the growing popularity of plant-based diets, challenges and social acceptance persist. Vegetarians encounter difficulties finding suitable food options in certain social settings and face skepticism or criticism from those who do not understand their dietary choices. However, increased awareness of plant-based diets has fostered greater acceptance and the availability of vegetarian-friendly options in many communities. Further, the rise of social media and online communities centered around plant-based lifestyles has also provided support networks and resources for individuals navigating the challenges associated with their dietary choices.
In conclusion, recognizing the diversity within plant-based diets is essential to assess the adequacy of its diet, but undoubtedly well-planned and diverse plant-based diets offer numerous health benefits, including a reduced risk of chronic diseases and improved overall nutrition. Additionally, the decision to adopt a plant-based diet often extends beyond personal health considerations, encompassing ethical and environmental motivations which although they have faced challenges being socially appreciated, the increasing awareness of vegetarianism has led to a broader acceptance and availability of plant-based options. Understanding the distinct nuances of different plant-based diets empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices that align with their health, values, and aspirations for a sustainable future. It may still appear for some as a unnecessary constrain vegetarians are putting themselves, but aspired from the vegetarian movement, we must all start making more carefully considered choices regarding our carnivore diets and their consequences.
References
- Marrone G, Guerriero C, Palazzetti D, Lido P, Marolla A, Di Daniele F, Noce A. Vegan Diet Health Benefits in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2021; 13(3):817.
- (2017) Vegan diets: practical advice for athletes and exercisers, Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14:1
- Intake and adequacy of the vegan diet. A systematic review of the evidence, Bakaloudi, Dimitra Rafailia et al. Clinical Nutrition, Volume 40, Issue 5, 3503 – 3521




