By Evanthia Vasiliki Tagari,
Who could have imagined waking up daily without enjoying their favorite cup of coffee? Definitely nο one. And not only could they not, but they would not want to, as the morning coffee for many of us connects us with our spiritual vigilance and not unjustly. Statistical studies have shown that more than 400 billion cups of coffee are consumed annually worldwide, with Finland, Sweden, and Switzerland leading the way. However, coffee has not accidentally flooded the market as the number one beverage in the world, but its composition and specifically the levels of caffeine contained in its beans or in the leaves of some types of tea, are responsible for our voluntary “addiction” to it.
Caffeine: Chemical formula and definition
Caffeine, or 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine with molecular structure C8H10N4O2, is a central nervous system stimulant of the methylxanthine class. Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, and has been described as the most widely used psychoactive drug in the world. Unlike many other psychoactive substances, it is legal and its consumption is not regulated in almost all parts of the world. It is found in the seeds, fruits, nuts, or leaves of a number of plants from Africa, East Asia, and South America and helps protect them from herbivores and competition by preventing the germination of nearby seeds, as well as encouraging consumption by selected animals, such as bees. The best known source of caffeine is coffee bean. To make these drinks, caffeine is extracted by immersing the plant product in water, a process called extraction.
How does it work?
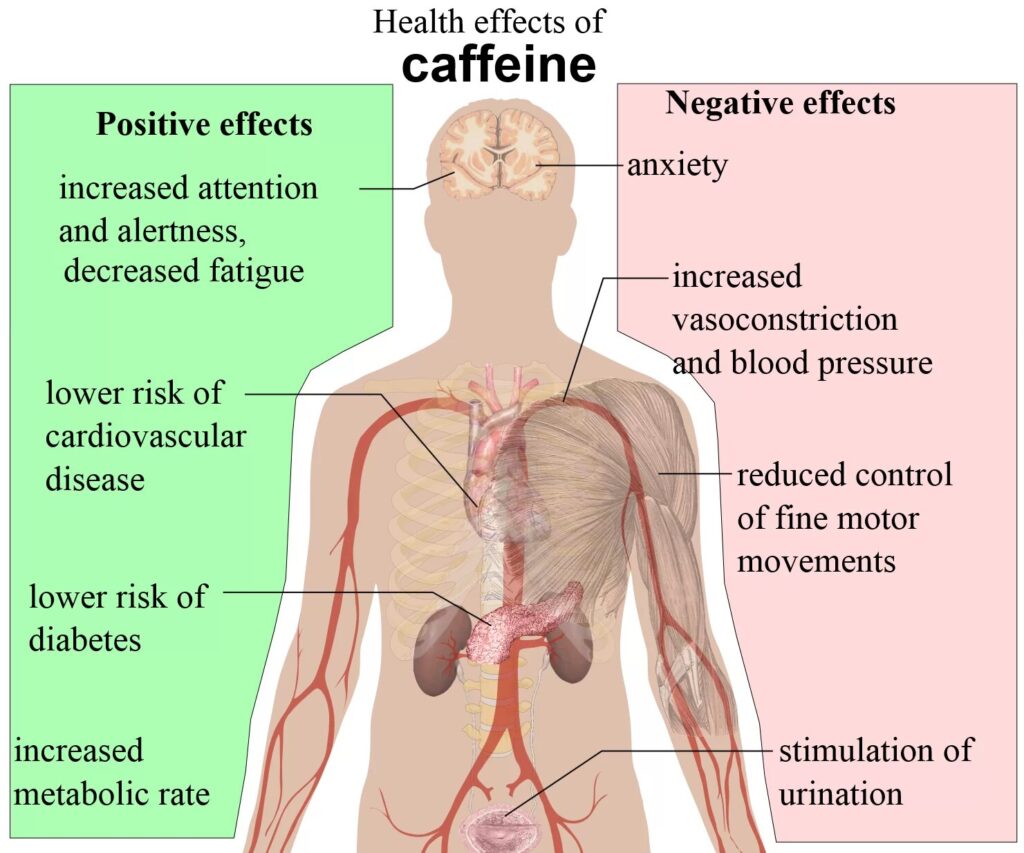
Once consumed, caffeine is rapidly absorbed from the intestine into the bloodstream. From there, it is transported to the liver where it breaks down into compounds that can affect the function of various organs. The mainly affected human organ is the brain. More specifically, caffeine works by blocking the effects of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that is responsible for feeling tired and relaxed during the day. Caffeine acts as an inhibitor of the normal action of adenosine in the body as it blocks its action on its receptors thus preventing the occurrence of drowsiness. The action of caffeine in the body is not limited there, but it can increase the levels of adrenaline in the blood while stimulating the brain activity of neurotransmitters, dopamine, and norepinephrine. This combination further stimulates the brain and promotes a state of arousal, alertness, and focus. The temporal response of caffeine in the body is relatively immediate, since an amount of a cup of coffee can be fully effective in the body within 1 hour.
Positive effects of caffeine consumption
Certainly, caffeine responds directly to our body by offering all those pleasant emotions we need to get through our day temporarily. However, the action of caffeine on the body can have extremely beneficial long-term effects on people’s health as well, when it is consumed at normal levels on a daily basis. Some of these positive effects are:
- Protection against heart disease and diabetes
Although coffee has generally been blamed for raising blood pressure, studies have shown that people who consume a controlled amount of coffee daily (100-400 mg) are up to 18% less likely to have a heart attack. In the same context, it has been shown that the risk of developing type II diabetes is reduced by a percentage of 14% for every 200 mg of coffee consumed daily.
- Boost metabolism and burn fat
Due to its ability to stimulate the central nervous system, caffeine can increase metabolism by up to 11% and fat burning by up to 13%. In practice, consuming 300 mg of caffeine a day can allow you to burn an extra 79 calories per day.
Other positive effects of coffee include protecting the liver, preventing cancers such as colon cancer, and protecting against multiple sclerosis. In general, coffee is largely associated with longevity and a reduction in the probability of premature death of up to 30%.

Unsafe caffeine consumption and side effects
Whilst generally the consumption of caffeine is considered to be safe, uncontrolled consumption can lead to addiction as it has been reported to be a psychoactive drug. The side effects that may occur are related to its excessive intake and relate to the feeling of anxiety, palpitations, inability to sleep and generally a turbulent condition for the body. Headaches, migraines and high blood pressure can also occur in people who consume high amounts of coffee daily. Special care is needed in pregnant women as caffeine can become dangerous as it binds to the placenta passing to the baby. The concomitant consumption of caffeine with specific muscle relaxants and antidepressants, is able to affect their action with negative effects on the body.
Conclusion
Caffeinated beverages, with the main representative the well-known coffee, can be extremely beneficial for the body, especially when we experience a feeling of fatigue. Nevertheless, and given that the action of caffeine ends up in the brain, its controlled consumption is necessary to maintain a mental and physical balance. According to both the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), the recommended portion of coffee consumption should not exceed 4 cups (<400 mg) per day. Because as always, we should take care of things in order to enjoy them!
References
- Better Health Channel, Caffeine, Available here
- e-importz.com, Coffee Statistics 2021, Available here
- Petre, A., What is Caffeine and is it good or bad for Health?, Healthline.com, Available here




